Finding the perfect educational path for your child is a common concern among parents and educators. With so many different methods and philosophies available, it can be overwhelming to decide which approach will best suit your child’s needs and nurture their potential. Today, we’ll explore two popular but distinctly different educational models—Montessori and traditional education. By understanding their core principles, key differences, and unique benefits, you’ll be better equipped to make an informed decision for your child’s future.
Table of Contents
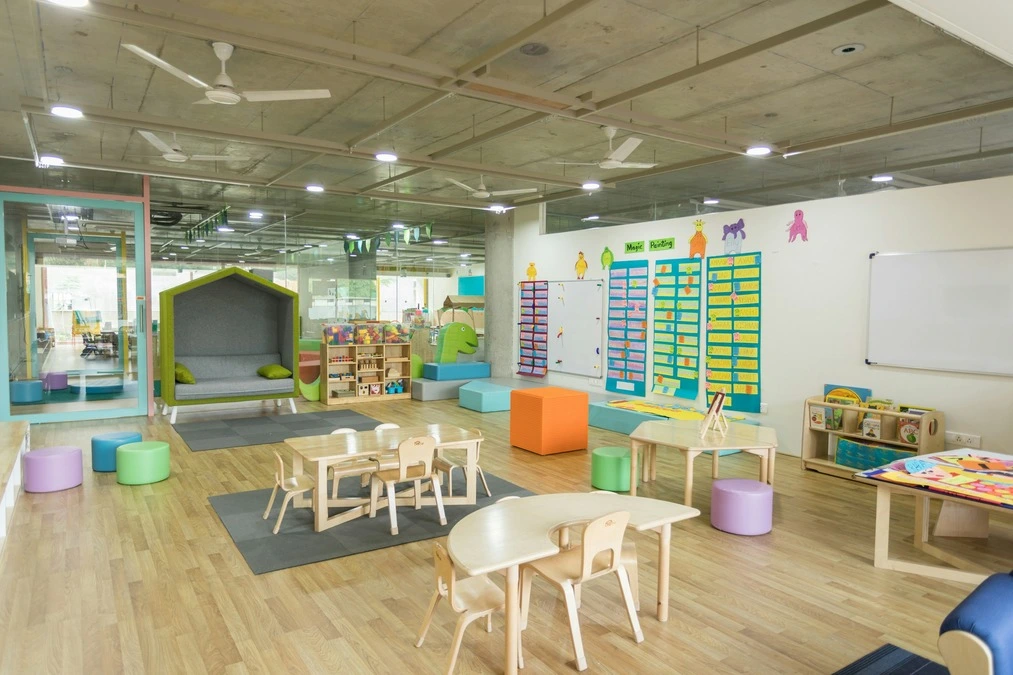
Montessori Education: An Overview
Montessori education is a child-centered approach developed by Dr. Maria Montessori in the early 20th century. Unlike traditional education, Montessori focuses on fostering independence, self-paced learning, and hands-on experiences. This educational model aims to cultivate a child’s natural curiosity and intrinsic motivation to learn.
Child-Centered Approach
In a Montessori classroom, children have the freedom to choose their activities and work at their own pace. The environment is meticulously prepared to meet the developmental needs of each child, encouraging them to take responsibility for their learning and explore subjects that interest them.
Independence and Exploration
A key aspect of Montessori education is promoting independence. Children are encouraged to make choices, solve problems, and manage their time effectively. This sense of autonomy not only boosts their confidence but also prepares them for real-world challenges.
Hands-On Materials and Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is at the heart of Montessori education. Classrooms are equipped with specialized materials designed to engage the senses and facilitate hands-on learning. These materials help children grasp abstract concepts through concrete experiences, making learning both fun and meaningful.
Traditional Education: An Overview
Traditional education, the most common model in schools worldwide, is characterized by a structured curriculum, standardized assessments, and a teacher-centered approach. Let’s take a closer look at its foundational elements.
Teacher-Centered Model
In traditional classrooms, teachers play a central role in delivering content and guiding students through a predetermined syllabus. This approach often involves direct instruction, where the teacher explains concepts, assigns tasks, and evaluates student performance.
Structured Curriculum and Standardized Assessments
Traditional education follows a set curriculum with specific learning objectives and timelines. Students are expected to complete assigned tasks and assessments within these parameters. Standardized tests are frequently used to measure academic progress and proficiency.
Focus on Rote Learning and Set Schedules
Traditional education often emphasizes rote learning, where students memorize information and follow a strict schedule. This method aims to prepare students for standardized tests and future academic endeavors by providing a clear structure and routine.
Key Differences Between Montessori and Traditional Education
Understanding the key differences between Montessori and traditional education can help you determine which approach aligns better with your child’s needs and your family’s values.
Learning Pace
Montessori education allows children to learn at their own pace, promoting self-directed exploration and discovery. In contrast, traditional education follows a teacher-guided pace, where all students progress through the curriculum simultaneously.
Classroom Environment
Montessori classrooms are designed to be welcoming and adaptable, with child-sized furniture and accessible materials. The environment encourages movement and collaboration. Traditional classrooms, on the other hand, often have structured seating arrangements with desks arranged in rows.
Curriculum Flexibility
A Montessori curriculum is personalized to each child’s interests and developmental stage. This flexibility allows for a more tailored educational experience. Traditional education relies on a standardized syllabus that all students must follow.
Teacher’s Role
In a Montessori setting, teachers act as guides and observers, facilitating learning without dictating it. They provide support and resources as needed. Conversely, traditional teachers are direct instructors, responsible for delivering content and managing classroom behavior.
Assessment Methods
Montessori assessments focus on observation, portfolios, and student self-reflection. This holistic approach evaluates a child’s progress and development over time. Traditional education relies heavily on grades and standardized tests to measure academic achievement.
Benefits of Montessori Education
Montessori education offers a range of benefits that can significantly impact a child’s development and lifelong learning habits.
Fosters Independence, Creativity, and Critical Thinking
By encouraging self-directed learning and problem-solving, Montessori education nurtures independent thinkers who are capable of creative and critical thought.
Encourages Intrinsic Motivation and Love for Learning
Montessori students develop an intrinsic love for learning, as they are free to explore subjects that genuinely interest them. This natural curiosity leads to deeper engagement and retention of information.
Social-Emotional Development Through Mixed-Age Classrooms
Montessori classrooms often include mixed-age groups, allowing younger children to learn from older peers and fostering a sense of community. This setup promotes social-emotional growth and collaboration.
Cultivates Lifelong Learning Habits
The skills and habits developed in a Montessori environment—such as self-discipline, time management, and a love for learning—prepare students for success in all areas of life.
Benefits of Traditional Education
While traditional education has its limitations, it also offers several advantages that can benefit students in various ways.
Provides Clear Structure and Benchmarks
A structured curriculum and clear benchmarks help students understand what is expected of them and track their progress. This structure can provide a sense of security and stability.
Prepares Students for Standardized Testing and Competitive Environments
Traditional education often places a strong emphasis on preparing students for standardized tests and competitive academic settings. This focus can help students develop the skills needed to excel in such environments.
Familiarity with Traditional Schooling Models
For many parents and educators, traditional schooling is a familiar and comfortable model. This familiarity can make it easier to support and engage with a child’s education.
Access to Extracurricular Activities and Social Networks
Traditional schools typically offer a wide range of extracurricular activities, sports, and social opportunities. These experiences can enrich a child’s education and help them develop well-rounded social skills.
Which Approach is Right for Your Child?
Choosing between Montessori and traditional education depends on various factors, including your child’s personality, learning style, and your family’s values.
Factors to Consider
Consider your child’s strengths, interests, and preferences when evaluating educational options. Some children thrive in a structured environment, while others excel in a more flexible and self-directed setting.
Blending Montessori Principles at Home
Even if you choose a traditional school, you can incorporate Montessori principles at home. Encourage independence, provide hands-on learning opportunities, and create a nurturing environment that supports your child’s growth.
Hybrid Education Models
Some schools offer hybrid education models that combine elements of both Montessori and traditional education. These programs can provide the best of both worlds, allowing for a more customized learning experience.
Conclusion
Ultimately, there is no “one-size-fits-all” approach to education. Both Montessori and traditional education have their unique strengths and challenges. The key is to find the right fit for your child’s individual needs and your family’s values. By understanding the differences and benefits of each model, you can make an informed decision that supports your child’s development and well-being.
If you’re still unsure which path to take, consider visiting local schools, talking to educators, and observing classrooms in action. Additionally, speaking with other parents and reading reviews can provide valuable insights. Remember, the goal is to create a supportive and enriching learning environment that empowers your child to reach their full potential.
Additional Resources
For further reading and in-depth analysis of Montessori and traditional education, consider visiting the following sources:
- American Montessori Society: A comprehensive resource on Montessori educational principles, training, and practices.
- National Center for Education Statistics: Offers data and reports on education systems, including insights on traditional schooling methodologies.
- The Montessori Foundation: Provides resources, articles, and research on Montessori education and its impact on child development.
- Harvard Education Publishing Group: Explore educational research and articles that highlight various teaching methods, including comparisons between Montessori and traditional education.
- Edutopia: A platform promoting innovative teaching strategies and practices across diverse educational settings, including Montessori approaches.